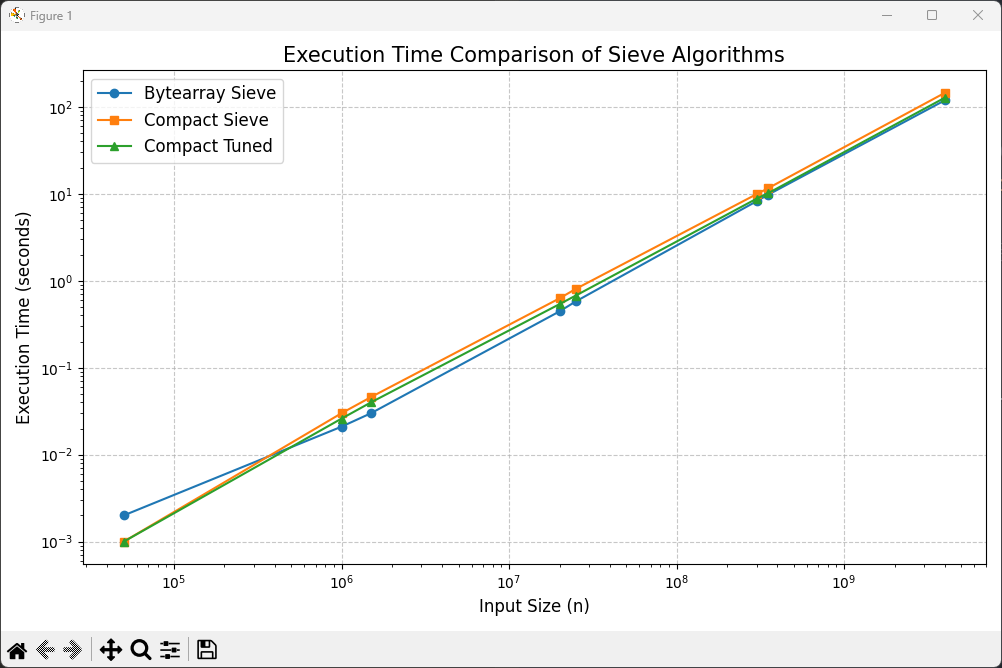
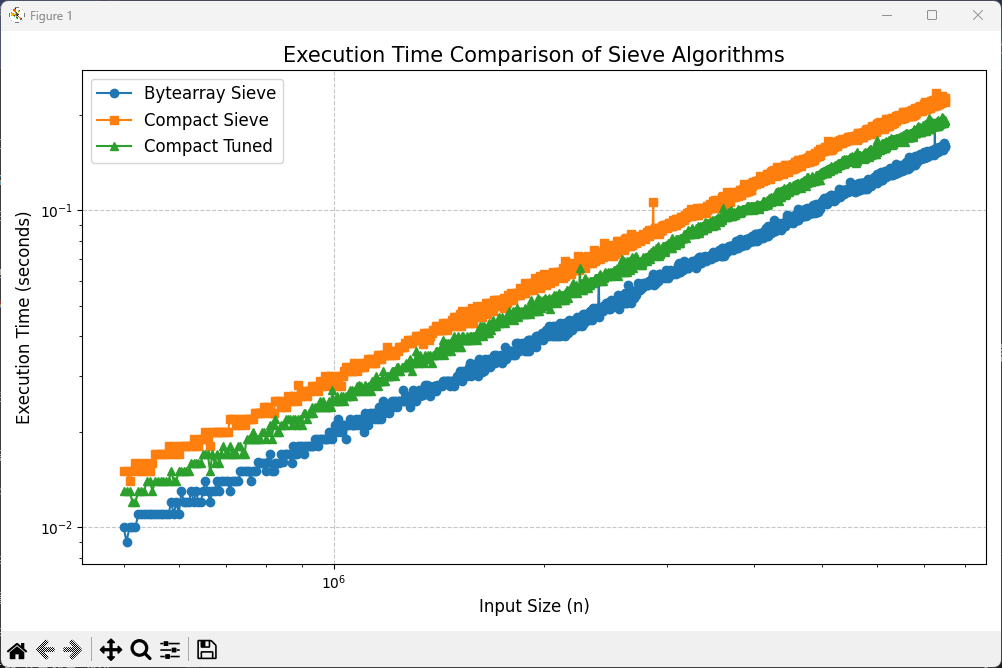
바이트 배열을 이용한 에라토스테네스의 체가 가장 빠르다는 실험을 했는데 다른 방법을 찾았다.
바이트 배열에 홀수만 저장하는 것이다.
메모리를 반만 쓸 수 있다.
그리고 온라인 저지 상에서는 더 빨랐다.
실제로는 좀 더 느리지만 근소한 차이를 보였다.
메모리까지 종합적으로 보면 더 우수하다고 할 수 있다.
그리고 내가 살짝 튠을 해 보니 조금 더 빠르게 할 수 있었다.
import time
import math
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def sieve_bytearray(n):
"""
# bytearray를 활용한 에라토스테네스의 체
# 메모리와 연산을 최적화하기 위해 bytearray 사용
"""
if n < 2:
return []
sieve = bytearray(b'\x01') * (n + 1)
sieve[0] = sieve[1] = 0
for i in range(2, int(math.sqrt(n)) + 1):
if sieve[i]:
sieve[i * i:n + 1:i] = bytearray(len(sieve[i * i:n + 1:i]))
return [i for i, is_prime in enumerate(sieve) if is_prime]
def sieve_compact(n):
"""
# 압축된 에라토스테네스의 체
# 바이트 배열(memoryview), 홀수만 저장, 메모리 최적화 버전
"""
if n < 2:
return []
# 2는 별도로 처리
if n == 2:
return [2]
# 최대 숫자를 저장할 수 있는 크기 계산 (홀수만 저장하므로 절반)
max_size = (n + 1) // 2
# 바이트 배열 초기화 (1로 채움)
c = memoryview(bytearray([1]) * max_size)
# 홀수 소수만 체크 (2는 별도 처리)
sqrt_limit = int(((int(n ** 0.5) - 3) // 2) + 1)
sqrt_limit = max(1, sqrt_limit) # 최소 1 이상으로 설정
for i in range(sqrt_limit):
if c[i]:
# i번째 홀수에 해당하는 수는 2*i+3
prime = 2 * i + 3
# 해당 수의 배수 제거 - 임시 배열 없이 직접 0으로 설정
start_idx = 2 * i * (i + 3) + 3
if start_idx < max_size:
for j in range(start_idx, max_size, 2 * i + 3):
c[j] = 0
# 소수 목록 생성 (2와 홀수 소수들)
primes = [2] # 2는 별도로 추가
# 홀수 중 소수인 것들 추가 (c[i] == 1인 경우)
for i in range(max_size):
if c[i]:
prime = 2 * i + 3
if prime > n: # n보다 큰 경우 제외
break
primes.append(prime)
return primes
def sieve_compact_tuned(n):
"""
# 더 최적화된 압축 에라토스테네스의 체
# 비트 시프트 연산, bytearray 직접 사용, math.isqrt 활용
"""
if n < 2:
return []
if n == 2:
return [2]
max_size = (n + 1) >> 1 # 홀수만 저장하므로 n/2 정도의 공간만 필요
c = bytearray([1]) * max_size # bytearray를 직접 사용 (메모리뷰 대신)
# 정수 제곱근 사용 (math.isqrt)
sqrt_n = math.isqrt(n)
# 2*i+3 가 sqrt_n 이하인 최대 i 계산 (p = 2*i+3 이므로)
sqrt_limit = ((sqrt_n - 3) >> 1) + 1 if sqrt_n >= 3 else 0
sqrt_limit = max(1, sqrt_limit)
for i in range(sqrt_limit):
if c[i]:
p = (i << 1) + 3 # 해당 인덱스에 대응하는 소수 후보
# p^2의 인덱스: (p^2 - 3) // 2
start_idx = (p * p - 3) >> 1
step = p # 홀수만 저장하므로 배수 간격은 p 단위
# for문으로 배수 제거 (안정적)
for j in range(start_idx, max_size, step):
c[j] = 0
# n 이하의 홀수에 해당하는 인덱스 범위 미리 계산: (n-3)//2 + 1
max_index = ((n - 3) >> 1) + 1
# 2는 별도로 추가하고, 나머지는 list comprehension으로 처리
primes = [2] + [(i << 1) + 3 for i in range(max_index) if c[i]]
return primes
def compare_algorithms(sizes, measure_real_memory=False):
"""
두 알고리즘의 성능을 비교하고 결과를 반환하는 함수
"""
results = {
'Bytearray Sieve': {'sizes': [], 'times': [], 'prime_counts': [], 'memory': []},
'Compact Sieve': {'sizes': [], 'times': [], 'prime_counts': [], 'memory': []}
}
algorithms = [
('Bytearray Sieve', sieve_bytearray),
('Compact Sieve', sieve_compact)
]
for size in sizes:
print(f"\n크기 {size:,}에 대한 성능 측정 중...")
for name, algorithm in algorithms:
# 시간 측정 시작
start_time = time.time()
try:
# 알고리즘 실행
primes = algorithm(size)
elapsed_time = time.time() - start_time
# 메모리 사용량 계산 (정확한 추정값)
if name == 'Bytearray Sieve':
# 바이트 어레이 체는 0~n까지 모든 숫자에 대해 1바이트씩 사용
memory_usage = size + 1 # 바이트 단위
else:
# 컴팩트 체는 홀수만 저장하므로 (n+1)/2 바이트만 사용
memory_usage = (size + 1) // 2 # 바이트 단위
# 결과 저장
results[name]['sizes'].append(size)
results[name]['times'].append(elapsed_time)
results[name]['prime_counts'].append(len(primes))
results[name]['memory'].append(memory_usage)
print(f" {name}: {len(primes):,}개 소수 찾음, {elapsed_time:.6f}초 소요, 메모리 예상: {memory_usage / 1024:.2f} KB")
except Exception as e:
print(f" {name}: 오류 발생 - {str(e)}")
results[name]['sizes'].append(size)
results[name]['times'].append(None)
results[name]['prime_counts'].append(None)
results[name]['memory'].append(None)
return results
def plot_comparison(results):
"""
비교 결과를 그래프로 그리는 함수
"""
# 알고리즘별 색상 및 마커 정의
colors = {
'Bytearray Sieve': '#1f77b4',
'Compact Sieve': '#ff7f0e',
'Compact Tuned': '#2ca02c'
}
markers = {
'Bytearray Sieve': 'o',
'Compact Sieve': 's',
'Compact Tuned': '^'
}
# 1. 실행 시간 비교 그래프
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6))
for name, data in results.items():
valid_indices = [i for i, t in enumerate(data['times']) if t is not None]
if not valid_indices:
continue
valid_sizes = [data['sizes'][i] for i in valid_indices]
valid_times = [data['times'][i] for i in valid_indices]
plt.plot(
valid_sizes,
valid_times,
marker=markers.get(name, 'o'),
linestyle='-',
color=colors.get(name, 'black'),
label=name
)
plt.title('Execution Time Comparison of Sieve Algorithms', fontsize=15)
plt.xlabel('Input Size (n)', fontsize=12)
plt.ylabel('Execution Time (seconds)', fontsize=12)
plt.grid(True, linestyle='--', alpha=0.7)
plt.legend(fontsize=12)
plt.yscale('log')
plt.xscale('log')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.savefig("sieve_time_comparison.png", dpi=300, bbox_inches='tight')
# 2. 메모리 사용량 비교 그래프
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6))
for name, data in results.items():
valid_indices = [i for i, m in enumerate(data['memory']) if m is not None]
if not valid_indices:
continue
valid_sizes = [data['sizes'][i] for i in valid_indices]
valid_memory = [data['memory'][i] / 1024 for i in valid_indices] # KB 단위로 변환
plt.plot(
valid_sizes,
valid_memory,
marker=markers.get(name, 'o'),
linestyle='-',
color=colors.get(name, 'black'),
label=name
)
plt.title('Memory Usage Comparison of Sieve Algorithms', fontsize=15)
plt.xlabel('Input Size (n)', fontsize=12)
plt.ylabel('Memory Usage (KB)', fontsize=12)
plt.grid(True, linestyle='--', alpha=0.7)
plt.legend(fontsize=12)
plt.xscale('log')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.savefig("sieve_memory_comparison.png", dpi=300, bbox_inches='tight')
# 3. 상대적 성능 비교 (bytearray 대비 다른 알고리즘의 속도 비율)
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6))
# Bytearray Sieve를 기준으로 비교
base_algorithm = 'Bytearray Sieve'
for name, data in results.items():
if name == base_algorithm:
continue
relative_performance = []
sizes_for_relative = []
for i in range(len(results[base_algorithm]['times'])):
base_time = results[base_algorithm]['times'][i]
curr_time = data['times'][i]
if base_time is not None and curr_time is not None and base_time > 0:
time_ratio = curr_time / base_time
relative_performance.append(time_ratio)
sizes_for_relative.append(results[base_algorithm]['sizes'][i])
if relative_performance: # 데이터가 있는 경우에만 그래프 그리기
plt.plot(
sizes_for_relative,
relative_performance,
marker=markers.get(name, 'o'),
linestyle='-',
color=colors.get(name, 'black'),
label=f'{name} / {base_algorithm}'
)
plt.axhline(y=1.0, color='r', linestyle='--', alpha=0.7, label='Equal Performance')
plt.title('Relative Performance vs Bytearray Sieve', fontsize=15)
plt.xlabel('Input Size (n)', fontsize=12)
plt.ylabel('Time Ratio (Algorithm/Bytearray)', fontsize=12)
plt.grid(True, linestyle='--', alpha=0.7)
plt.legend(fontsize=10)
plt.xscale('log')
plt.ylim(0, 1.1) # 0~110% 범위로 설정 (1.0 이하가 더 빠른 것)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.savefig("sieve_relative_performance.png", dpi=300, bbox_inches='tight')
# 4. 메모리 절약률 그래프
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6))
# Bytearray Sieve를 기준으로 비교
for name, data in results.items():
if name == base_algorithm:
continue
relative_memory = []
sizes_for_memory = []
for i in range(len(results[base_algorithm]['memory'])):
base_mem = results[base_algorithm]['memory'][i]
curr_mem = data['memory'][i]
if base_mem is not None and curr_mem is not None and base_mem > 0:
memory_ratio = curr_mem / base_mem
relative_memory.append(memory_ratio)
sizes_for_memory.append(results[base_algorithm]['sizes'][i])
if relative_memory:
plt.plot(
sizes_for_memory,
relative_memory,
marker=markers.get(name, 'o'),
linestyle='-',
color=colors.get(name, 'black'),
label=f'{name} / {base_algorithm}'
)
plt.axhline(y=1.0, color='r', linestyle='--', alpha=0.7, label='Equal Memory Usage')
plt.axhline(y=0.5, color='g', linestyle='--', alpha=0.7, label='50% Usage (Ideal)')
plt.title('Memory Usage Ratio vs Bytearray Sieve', fontsize=15)
plt.xlabel('Input Size (n)', fontsize=12)
plt.ylabel('Memory Ratio (Algorithm/Bytearray)', fontsize=12)
plt.grid(True, linestyle='--', alpha=0.7)
plt.legend(fontsize=10)
plt.xscale('log')
plt.ylim(0, 1.1) # 0~110% 범위로 설정
plt.tight_layout()
plt.savefig("sieve_memory_ratio.png", dpi=300, bbox_inches='tight')
plt.show()
def print_summary(results):
"""
결과 요약 출력
"""
print("\n===== 성능 비교 요약 =====")
# 기준 알고리즘 (바이트어레이 체)
base_algorithm = 'Bytearray Sieve'
base_data = results[base_algorithm]
# 실행 시간 비교
print("\n크기별 실행 시간 (초):")
headers = [f"{'크기':>10}"]
for name in results.keys():
headers.append(f"{name:>15}")
# 상대 비율 헤더 추가
for name in results.keys():
if name != base_algorithm:
headers.append(f"{name + '/기준':>15}")
print(" | ".join(headers))
print("-" * (15 * (2 * len(results.keys()) - 1) + 10))
for i in range(len(base_data['sizes'])):
size = base_data['sizes'][i]
row = [f"{size:>10,}"]
# 각 알고리즘의 실행 시간
time_values = {}
for name, data in results.items():
if i < len(data['times']) and data['times'][i] is not None:
time_values[name] = data['times'][i]
row.append(f"{data['times'][i]:>15.6f}")
else:
row.append(f"{'-':>15}")
# 상대 비율
base_time = time_values.get(base_algorithm)
if base_time:
for name, data in results.items():
if name != base_algorithm:
if name in time_values and time_values[name] > 0:
ratio = time_values[name] / base_time
row.append(f"{ratio:>15.3f}")
else:
row.append(f"{'-':>15}")
print(" | ".join(row))
# 메모리 사용량 비교
print("\n크기별 메모리 사용량 (KB):")
headers = [f"{'크기':>10}"]
for name in results.keys():
headers.append(f"{name:>15}")
# 상대 비율 헤더 추가
for name in results.keys():
if name != base_algorithm:
headers.append(f"{name + '/기준':>15}")
print(" | ".join(headers))
print("-" * (15 * (2 * len(results.keys()) - 1) + 10))
for i in range(len(base_data['sizes'])):
size = base_data['sizes'][i]
row = [f"{size:>10,}"]
# 각 알고리즘의 메모리 사용량 (KB)
memory_values = {}
for name, data in results.items():
if i < len(data['memory']) and data['memory'][i] is not None:
memory_kb = data['memory'][i] / 1024
memory_values[name] = memory_kb
row.append(f"{memory_kb:>15.2f}")
else:
row.append(f"{'-':>15}")
# 상대 비율
base_memory = memory_values.get(base_algorithm)
if base_memory:
for name, data in results.items():
if name != base_algorithm:
if name in memory_values and memory_values[name] > 0:
ratio = memory_values[name] / base_memory
row.append(f"{ratio:>15.3f}")
else:
row.append(f"{'-':>15}")
print(" | ".join(row))
# 소수 개수 일치 확인
print("\n크기별 찾은 소수 개수:")
headers = [f"{'크기':>10}"]
for name in results.keys():
headers.append(f"{name:>15}")
print(" | ".join(headers))
print("-" * (15 * len(results.keys()) + 10))
for i in range(len(base_data['sizes'])):
size = base_data['sizes'][i]
row = [f"{size:>10,}"]
counts = {}
for name, data in results.items():
if i < len(data['prime_counts']) and data['prime_counts'][i] is not None:
counts[name] = data['prime_counts'][i]
row.append(f"{data['prime_counts'][i]:>15,}")
else:
row.append(f"{'-':>15}")
print(" | ".join(row))
# 일치 여부 확인
if len(results) > 1:
print("\n소수 개수 일치 확인:")
print(f"{'크기':>10} | {'일치 여부':>15}")
print("-" * 30)
for i in range(len(base_data['sizes'])):
size = base_data['sizes'][i]
base_count = base_data['prime_counts'][i]
all_match = True
for name, data in results.items():
if name != base_algorithm:
if i < len(data['prime_counts']) and data['prime_counts'][i] != base_count:
all_match = False
break
match_str = "모두 일치" if all_match else "불일치"
print(f"{size:>10,} | {match_str:>15}")
# 평균 성능 비교
print("\n알고리즘별 기준 대비 평균 성능:")
print(f"{'알고리즘':>15} | {'평균 시간 비율':>15} | {'평균 메모리 비율':>15} | {'시간 단축':>15} | {'메모리 절약':>15}")
print("-" * 85)
for name, data in results.items():
if name == base_algorithm:
continue
valid_time_ratios = []
valid_memory_ratios = []
for i in range(len(base_data['sizes'])):
if i < len(base_data['times']) and i < len(data['times']):
base_time = base_data['times'][i]
curr_time = data['times'][i]
if base_time is not None and curr_time is not None and base_time > 0:
time_ratio = curr_time / base_time
valid_time_ratios.append(time_ratio)
if i < len(base_data['memory']) and i < len(data['memory']):
base_mem = base_data['memory'][i]
curr_mem = data['memory'][i]
if base_mem is not None and curr_mem is not None and base_mem > 0:
memory_ratio = curr_mem / base_mem
valid_memory_ratios.append(memory_ratio)
if valid_time_ratios:
avg_time_ratio = sum(valid_time_ratios) / len(valid_time_ratios)
time_saving = (1 - avg_time_ratio) * 100
time_ratio_str = f"{avg_time_ratio:.3f}:1"
time_saving_str = f"{time_saving:.1f}%" if time_saving > 0 else f"{-time_saving:.1f}% 느림"
else:
time_ratio_str = "-"
time_saving_str = "-"
if valid_memory_ratios:
avg_memory_ratio = sum(valid_memory_ratios) / len(valid_memory_ratios)
memory_saving = (1 - avg_memory_ratio) * 100
memory_ratio_str = f"{avg_memory_ratio:.3f}:1"
memory_saving_str = f"{memory_saving:.1f}%"
else:
memory_ratio_str = "-"
memory_saving_str = "-"
print(
f"{name:>15} | {time_ratio_str:>15} | {memory_ratio_str:>15} | {time_saving_str:>15} | {memory_saving_str:>15}")
# 튜닝 효과 분석 (Compact Tuned vs Compact Sieve)
if 'Compact Sieve' in results and 'Compact Tuned' in results:
print("\n최적화 효과 분석 (Compact Tuned vs Compact Sieve):")
valid_time_ratios = []
for i in range(len(results['Compact Sieve']['times'])):
if i < len(results['Compact Tuned']['times']):
base_time = results['Compact Sieve']['times'][i]
tuned_time = results['Compact Tuned']['times'][i]
if base_time is not None and tuned_time is not None and base_time > 0:
time_ratio = tuned_time / base_time
valid_time_ratios.append(time_ratio)
if valid_time_ratios:
avg_time_ratio = sum(valid_time_ratios) / len(valid_time_ratios)
tuning_effect = (1 - avg_time_ratio) * 100
print(f"튜닝된 버전은 기본 컴팩트 체보다 평균 {tuning_effect:.1f}% 더 빠릅니다.")
if tuning_effect > 0:
print(f"비트 시프트 연산, 정수 제곱근, 루프 최적화 등이 성능 향상에 기여했습니다.")
else:
print(f"튜닝이 오히려 {-tuning_effect:.1f}% 성능을 저하시켰습니다. 알고리즘 확인이 필요합니다.")
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 테스트할 입력 크기 목록
test_sizes = [50000*i*10**(i>>1)for i in range(1,9)]
# 알고리즘 목록 확장 - 튜닝된 버전 추가
algorithms = [
('Bytearray Sieve', sieve_bytearray),
('Compact Sieve', sieve_compact),
('Compact Tuned', sieve_compact_tuned)
]
# 결과 저장소 초기화
results = {name: {"sizes": [], "times": [], "prime_counts": [], "memory": []} for name, _ in algorithms}
# 알고리즘 성능 비교 실행
print("세 가지 알고리즘 성능 비교 시작...")
for size in test_sizes:
print(f"\n크기 {size:,}에 대한 성능 측정 중...")
for name, algorithm in algorithms:
# 시간 측정 시작
start_time = time.time()
try:
# 알고리즘 실행
primes = algorithm(size)
elapsed_time = time.time() - start_time
# 메모리 사용량 계산 (정확한 추정값)
if name == 'Bytearray Sieve':
# 바이트 어레이 체는 0~n까지 모든 숫자에 대해 1바이트씩 사용
memory_usage = size + 1 # 바이트 단위
else:
# 컴팩트 체는 홀수만 저장하므로 (n+1)/2 바이트만 사용
memory_usage = (size + 1) // 2 # 바이트 단위
# 결과 저장
results[name]['sizes'].append(size)
results[name]['times'].append(elapsed_time)
results[name]['prime_counts'].append(len(primes))
results[name]['memory'].append(memory_usage)
print(f" {name}: {len(primes):,}개 소수 찾음, {elapsed_time:.6f}초 소요, 메모리 예상: {memory_usage / 1024:.2f} KB")
except Exception as e:
print(f" {name}: 오류 발생 - {str(e)}")
results[name]['sizes'].append(size)
results[name]['times'].append(None)
results[name]['prime_counts'].append(None)
results[name]['memory'].append(None)
# 결과 요약 출력
print_summary(results)
# 그래프 그리기
print("\n그래프를 생성하는 중...")
plot_comparison(results)
print("\n비교 완료!")
세 가지 알고리즘 성능 비교 시작...
크기 50,000에 대한 성능 측정 중...
Bytearray Sieve: 5,133개 소수 찾음, 0.002001초 소요, 메모리 예상: 48.83 KB
Compact Sieve: 5,133개 소수 찾음, 0.000999초 소요, 메모리 예상: 24.41 KB
Compact Tuned: 5,133개 소수 찾음, 0.000999초 소요, 메모리 예상: 24.41 KB
크기 1,000,000에 대한 성능 측정 중...
Bytearray Sieve: 78,498개 소수 찾음, 0.021001초 소요, 메모리 예상: 976.56 KB
Compact Sieve: 78,498개 소수 찾음, 0.029999초 소요, 메모리 예상: 488.28 KB
Compact Tuned: 78,498개 소수 찾음, 0.026000초 소요, 메모리 예상: 488.28 KB
크기 1,500,000에 대한 성능 측정 중...
Bytearray Sieve: 114,155개 소수 찾음, 0.029999초 소요, 메모리 예상: 1464.84 KB
Compact Sieve: 114,155개 소수 찾음, 0.046000초 소요, 메모리 예상: 732.42 KB
Compact Tuned: 114,155개 소수 찾음, 0.040001초 소요, 메모리 예상: 732.42 KB
크기 20,000,000에 대한 성능 측정 중...
Bytearray Sieve: 1,270,607개 소수 찾음, 0.444001초 소요, 메모리 예상: 19531.25 KB
Compact Sieve: 1,270,607개 소수 찾음, 0.626998초 소요, 메모리 예상: 9765.62 KB
Compact Tuned: 1,270,607개 소수 찾음, 0.538001초 소요, 메모리 예상: 9765.62 KB
크기 25,000,000에 대한 성능 측정 중...
Bytearray Sieve: 1,565,927개 소수 찾음, 0.577999초 소요, 메모리 예상: 24414.06 KB
Compact Sieve: 1,565,927개 소수 찾음, 0.805000초 소요, 메모리 예상: 12207.03 KB
Compact Tuned: 1,565,927개 소수 찾음, 0.675001초 소요, 메모리 예상: 12207.03 KB
크기 300,000,000에 대한 성능 측정 중...
Bytearray Sieve: 16,252,325개 소수 찾음, 8.192661초 소요, 메모리 예상: 292968.75 KB
Compact Sieve: 16,252,325개 소수 찾음, 9.884632초 소요, 메모리 예상: 146484.38 KB
Compact Tuned: 16,252,325개 소수 찾음, 8.760999초 소요, 메모리 예상: 146484.38 KB
크기 350,000,000에 대한 성능 측정 중...
Bytearray Sieve: 18,803,526개 소수 찾음, 9.692507초 소요, 메모리 예상: 341796.88 KB
Compact Sieve: 18,803,526개 소수 찾음, 11.514000초 소요, 메모리 예상: 170898.44 KB
Compact Tuned: 18,803,526개 소수 찾음, 10.088999초 소요, 메모리 예상: 170898.44 KB
크기 4,000,000,000에 대한 성능 측정 중...
Bytearray Sieve: 189,961,812개 소수 찾음, 118.834210초 소요, 메모리 예상: 3906250.00 KB
Compact Sieve: 189,961,812개 소수 찾음, 144.888195초 소요, 메모리 예상: 1953125.00 KB
Compact Tuned: 189,961,812개 소수 찾음, 127.367038초 소요, 메모리 예상: 1953125.00 KB
===== 성능 비교 요약 =====
크기별 실행 시간 (초):
크기 | Bytearray Sieve | Compact Sieve | Compact Tuned | Compact Sieve/기준 | Compact Tuned/기준
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
50,000 | 0.002001 | 0.000999 | 0.000999 | 0.499 | 0.499
1,000,000 | 0.021001 | 0.029999 | 0.026000 | 1.428 | 1.238
1,500,000 | 0.029999 | 0.046000 | 0.040001 | 1.533 | 1.333
20,000,000 | 0.444001 | 0.626998 | 0.538001 | 1.412 | 1.212
25,000,000 | 0.577999 | 0.805000 | 0.675001 | 1.393 | 1.168
300,000,000 | 8.192661 | 9.884632 | 8.760999 | 1.207 | 1.069
350,000,000 | 9.692507 | 11.514000 | 10.088999 | 1.188 | 1.041
4,000,000,000 | 118.834210 | 144.888195 | 127.367038 | 1.219 | 1.072
크기별 메모리 사용량 (KB):
크기 | Bytearray Sieve | Compact Sieve | Compact Tuned | Compact Sieve/기준 | Compact Tuned/기준
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
50,000 | 48.83 | 24.41 | 24.41 | 0.500 | 0.500
1,000,000 | 976.56 | 488.28 | 488.28 | 0.500 | 0.500
1,500,000 | 1464.84 | 732.42 | 732.42 | 0.500 | 0.500
20,000,000 | 19531.25 | 9765.62 | 9765.62 | 0.500 | 0.500
25,000,000 | 24414.06 | 12207.03 | 12207.03 | 0.500 | 0.500
300,000,000 | 292968.75 | 146484.38 | 146484.38 | 0.500 | 0.500
350,000,000 | 341796.88 | 170898.44 | 170898.44 | 0.500 | 0.500
4,000,000,000 | 3906250.00 | 1953125.00 | 1953125.00 | 0.500 | 0.500
크기별 찾은 소수 개수:
크기 | Bytearray Sieve | Compact Sieve | Compact Tuned
-------------------------------------------------------
50,000 | 5,133 | 5,133 | 5,133
1,000,000 | 78,498 | 78,498 | 78,498
1,500,000 | 114,155 | 114,155 | 114,155
20,000,000 | 1,270,607 | 1,270,607 | 1,270,607
25,000,000 | 1,565,927 | 1,565,927 | 1,565,927
300,000,000 | 16,252,325 | 16,252,325 | 16,252,325
350,000,000 | 18,803,526 | 18,803,526 | 18,803,526
4,000,000,000 | 189,961,812 | 189,961,812 | 189,961,812
소수 개수 일치 확인:
크기 | 일치 여부
------------------------------
50,000 | 모두 일치
1,000,000 | 모두 일치
1,500,000 | 모두 일치
20,000,000 | 모두 일치
25,000,000 | 모두 일치
300,000,000 | 모두 일치
350,000,000 | 모두 일치
4,000,000,000 | 모두 일치
알고리즘별 기준 대비 평균 성능:
알고리즘 | 평균 시간 비율 | 평균 메모리 비율 | 시간 단축 | 메모리 절약
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Compact Sieve | 1.235:1 | 0.500:1 | 23.5% 느림 | 50.0%
Compact Tuned | 1.079:1 | 0.500:1 | 7.9% 느림 | 50.0%
최적화 효과 분석 (Compact Tuned vs Compact Sieve):
튜닝된 버전은 기본 컴팩트 체보다 평균 11.6% 더 빠릅니다.
비트 시프트 연산, 정수 제곱근, 루프 최적화 등이 성능 향상에 기여했습니다.
그래프를 생성하는 중...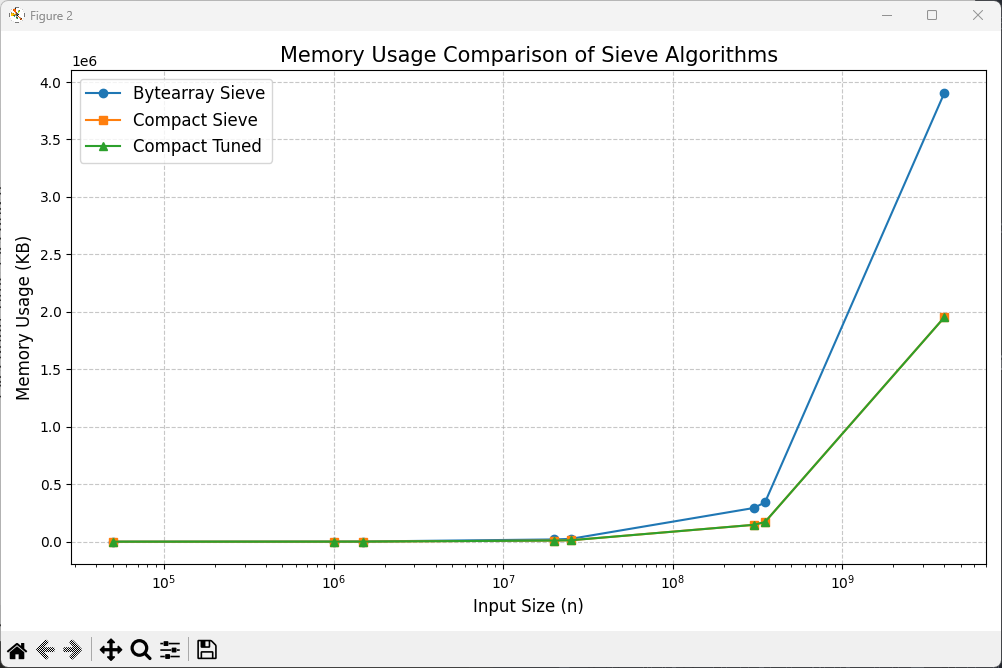
'Tech > Coding' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 에라스토테네스의 체 추가실험(로컬에서 실험) (0) | 2025.02.28 |
|---|---|
| 가우시안 소거법 (0) | 2025.02.25 |
| 벨만 포드 알고리즘 (0) | 2025.02.24 |
| 에라토스테네스의 체 (0) | 2025.02.24 |
| 1836🐨트리의 가짓수 세기 .py (0) | 2025.02.23 |



